Qt (pronounced 'cute') is a free and open-source widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces as well as cross-platform applications that run on various software and hardware platforms such as Linux, Windows, macOS, Android or embedded systems with little or no change in the underlying codebase while still being a native application with native capabilities and speed. Qt Creator is a full-featured cross-platform IDE for C programming (with or without the Qt libraries). Primarily intended for use with the Qt toolkit, but usable for general C/C development too.

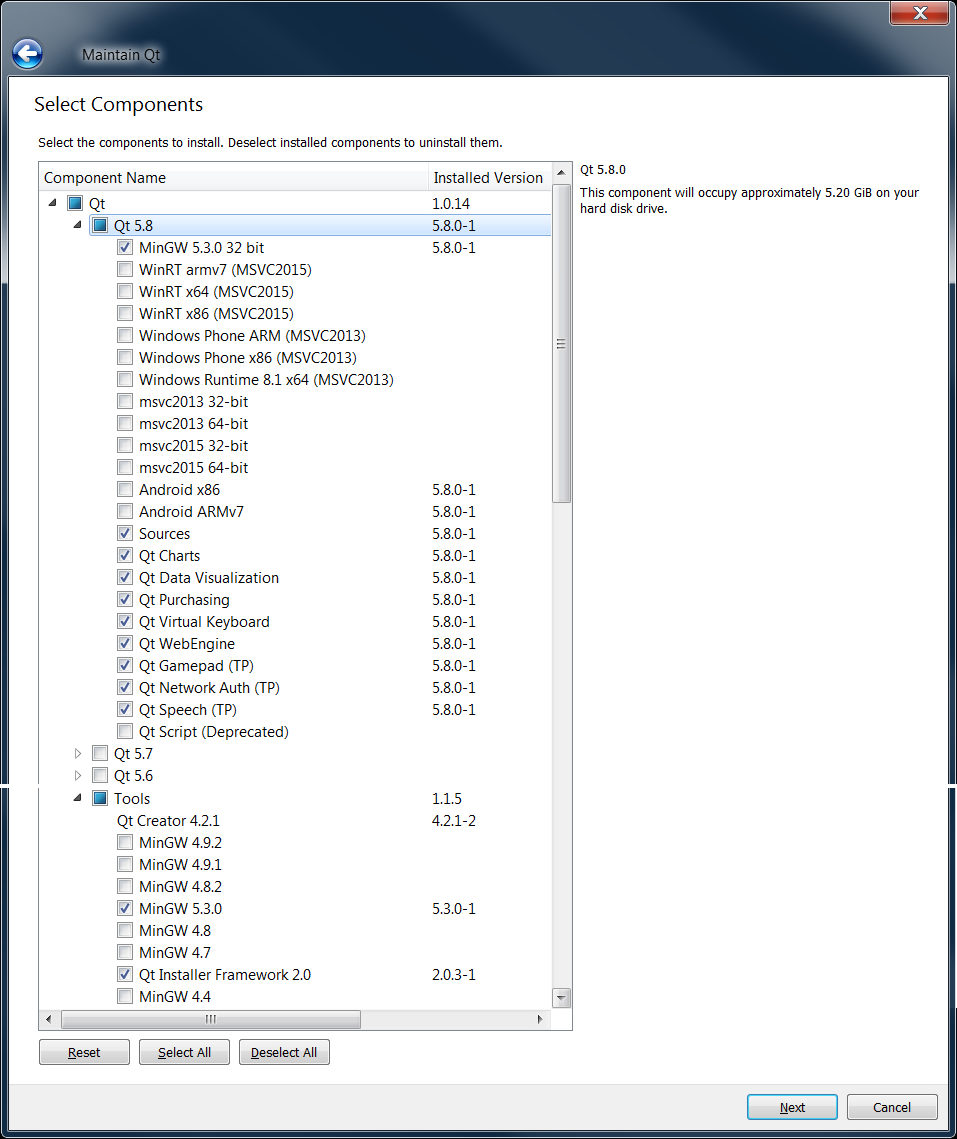
Downloading and Installing Qt
This is an example built with Basic For Qt® (and deployed from within its IDE) and contains all needed files (including the DLL files for Qt) and runs without installation procedure (as all applications created with Basic For Qt® are deployed with all needed files). Mac® Trial Basic For Qt® (V1.0) for Mac. For this question, I'm using Qt as an IDE. I'm not doing GUI code. I'm targeting Linux - I use a docker Ubuntu instance for builds, although I can also build under Mac with the same makefile. However, even though Make is entirely happy, Qt is not. Exit(0); Qt IDE complains about undefined identifier I've tried including stdlib.h. When the Qt tools are available from the command line, proceed to Creating a Simple Qt Application in this article. Setting Up Qt for NetBeans IDE on Solaris Platforms. Binaries for Qt are not available for Solaris platforms. However, it is possible to build the Qt libraries from sources that you can get from the official Qt source code repository.
There are two ways to install Qt:
- through the Qt Installers - downloads and installs Qt
- through the Qt sources.
You can download the Qt 5 installers and sources from the Downloads page. For more information, visit the Getting Started with Qt page.
Building Qt 5 from Source
Below, you will find more information about building Qt from source.
- Qt for macOS - Building from Source - building and installing from source
Note: Qt 5 uses Cocoa, therefore, building for Carbon is not possible.
macOS Versions

See Supported Platforms for the list of macOS versions supported by Qt.
Qt can be built for either x86 or x86_64. 64-bit is used by default. To select a 32-bit build, use the QMAKE_APPLE_DEVICE_ARCHSqmake variable. This is selectable at configure time:
QMAKE_APPLE_DEVICE_ARCHS can also be specified as a space-delimited list in order to build for multiple architectures simultaneously:
Note: Qt 5 does not support OS X on PowerPC.
Note: Static builds are not tested.
Additional Command-Line Options
On the command-line, applications can be built using qmake and make. Optionally, qmake can generate project files for Xcode with -spec macx-xcode. If you are using the binary package, qmake generates Xcode projects by default; use -spec macx-gcc to generate makefiles. For example:

Configuring with -spec macx-xcode generates an Xcode project file from project.pro. With qmake you do not have to worry about rules for Qt's preprocessors (moc and uic) since qmake automatically handles them and ensures that everything necessary is linked into your application.
Qt does not entirely interact with the development environment (for example plugins to set a file to 'mocable' from within the Xcode user interface).
The result of the build process is an application bundle, which is a directory structure that contains the actual application executable. The application can be launched by double-clicking it in Finder, or by referring directly to its executable from the command line, for example, myApp.app/Contents/MacOS/myApp.
If you wish to have a command-line tool that does not use the GUI for example, moc, uic or ls, you can tell qmake to disable bundle creation from the CONFIG variable in the project file:
Deploying Applications on macOS
In general, Qt supports building on one macOS version and deploying to earlier or later macOS versions. The recommended way is to build on the latest version and deploy to an earlier macOS version.
macOS applications are typically deployed as self-contained application bundles. The application bundle contains the application executable as well as dependencies such as the Qt libraries, plugins, translations and other resources you may need. Third party libraries like Qt are normally not installed system-wide; each application provides its own copy.
Discover the world of SSD Hard Drives for Mac. Compare models and options for the office or home and shop online. Upgrade nearly any Apple computer for faster speeds and more flash storage. SSD upgrade kits include all tools needed to safely upgrade your Mac. If you install an SSD on a Mac, it's important to make sure that the TRIM command is running on the machine. Screenshot by Dong Ngo If you have replaced the hard drive on your Mac with an SSD. Ssd drives for mac. Upgrade your MacBook Pro to an SSD for up to 6x the capacity and 106x the speed of the original drive. Includes DIY install videos to make upgrading easy.
A common way to distribute applications is to provide a compressed disk image (.dmg file) that the user can mount in Finder. The deployment tool, macdeployqt (available from the macOS installers), can be used to create the self-contained bundles, and optionally also create a .dmg archive. Applications can also be distributed through the Mac App Store. Qt 5 aims to stay within the app store sandbox rules. macdeployqt (bin/macdeployqt) can be used as a starting point for app store deployment.
macOS Issues
The page below covers specific issues and recommendations for creating macOS applications.
Where to Go from Here
We invite you to explore the rest of Qt. We prepared overviews to help you decide which APIs to use and our examples demonstrate how to use our API.

- Qt Overviews - list of topics about application development
- Examples and Tutorials - code samples and tutorials
- Qt Reference Pages - a listing of C++ and QML APIs
Qt's vibrant and active community site, http://qt.io houses a wiki, a forum, and additional learning guides and presentations.
© 2019 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
macOS (previously known as OS X or Mac OS X) is Apple's operating system for the Mac line of computers. It's a UNIX platform, based on the Darwin kernel, and behaves largely similar to other UNIX-like platforms. The main difference is that X11 is not used as the windowing system. Instead, macOS uses its own native windowing system that is accessible through the Cocoa API.
To download and install Qt for macOS, follow the instructions on the Getting Started with Qt page.
Supported Versions
When talking about version support on macOS, it's important to distinguish between the build environment; the platform you're building on or with, and the target platforms; the platforms you are building for. The following macOS versions are supported.
| Target Platform | Architecture | Build Environment |
|---|---|---|
| macOS 10.13, 10.14, 10.15 | x86_64 and x86_64h | Xcode 11 (10.15 SDK) |
Build Environment
The build environment on macOS is defined entirely by the Xcode version used to build your application. Xcode contains both a toolchain (compiler, linker, and other tools), and a macOS platform-SDK (headers and libraries). Together these define how your application is built.
Note: The version of macOS that you are running Xcode on does not matter. As long as Apple ships a given Xcode version that runs on your operating system, the build environment will be defined by that Xcode version.
Xcode can be downloaded from Apple's developer website (including older versions of Xcode). Once installed, choosing an Xcode installation is done using the xcode-select tool.
You can inspect the globally selected Xcode installation using the same tool.
The xcrun command can then be used to find a particular tool in the toolchain.
Its enhanced mouse control draws you deeper into the gaming experience to give you a more hand s-on —or rather, finger-on —approach. It can help you create high-quality vector graphics or produce true 1080p videos. For those who are avid gamers, you won't want to miss out on these fun perks.The software program also lets you watch videos in HD with industry-standard codecs such as H.264, AAC, and MP3. What is adobe flash player for mac.
or show the platform SDK path used when building.
Target Platforms
Building for macOS utilizes a technique called weak linking that allows you to build your application against the headers and libraries of the latest platform SDK, while still allowing your application to be deployed to macOS versions lower than the SDK version. When the binary is run on a macOS version lower than the SDK it was built with, Qt will check at runtime whether or not a platform feature is available before utilizing it.
In theory this would allow running your application on every single macOS version released, but for practical (and technical) reasons there is a lower limit to this range, known as the deployment target of your application. If the binary is launched on a macOS version below the deployment target macOS or Qt will give an error message and the application will not run.
Qt expresses the deployment target via the QMAKE_MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET qmake variable, which has a default value set via the makespec for macOS. You should not need to change this default, but if needed you can increase it in your project file:
Note: You should not lower the deployment target beyond the default value set by Qt. Doing so will likely lead to crashes at runtime if the binary is then deployed to a macOS version lower than what Qt expected to run on.
Qt Creator For Mac Download
By always building against the latest available platform SDK, you ensure that Qt can take advantage of new features introduced in recent versions of macOS.
For more information about SDK-based development on macOS, see Apple's developer documentation.
Qt Ide For Mac Installer
Opting out of macOS behavior changes
One caveat to using the latest Xcode version and SDK to build your application is that macOS's system frameworks will sometimes decide whether or not to enable behavior changes based on the SDK you built your application with.
For example, when dark-mode was introduced in macOS 10.14 Mojave, macOS would only treat applications built against the 10.14 SDK as supporting dark-mode, and would leave applications built against earlier SDKs with the default light mode look. This technique allows Apple to ensure that binaries built long before the new SDK and operating system was released will still continue to run without regressions on new macOS releases.
Qt Ide For Mac Catalina
Microsoft office for mac 2011 standard sp4. A consequence of this is that if Qt has problems dealing with some of these macOS features (dark-mode, layer-backed views), the only way to opt out of them is building with an earlier SDK (the 10.13 SDK, available through Xcode 9). This is a last-resort solution, and should only be applied if your application has no other ways of working around the problem.
Architectures
By default, Qt is built for x86_64. To build for x86_64h (Haswell). use the QMAKE_APPLE_DEVICE_ARCHSqmake variable. This is selectable at configure time:
QMAKE_APPLE_DEVICE_ARCHS can also be specified as a space-delimited list in order to build for multiple architectures simultaneously:
Additional Command-Line Options
On the command-line, applications can be built using qmake and make. Optionally, qmake can generate project files for Xcode with -spec macx-xcode. If you are using the binary package, qmake generates Xcode projects by default; use -spec macx-gcc to generate makefiles. For example:
Qt Ide For Mac Shortcut
Configuring with -spec macx-xcode generates an Xcode project file from project.pro. With qmake you do not have to worry about rules for Qt's preprocessors (moc and uic) since qmake automatically handles them and ensures that everything necessary is linked into your application.
Qt does not entirely interact with the development environment (for example plugins to set a file to 'mocable' from within the Xcode user interface).
The result of the build process is an application bundle, which is a directory structure that contains the actual application executable. The application can be launched by double-clicking it in Finder, or by referring directly to its executable from the command line, for example, myApp.app/Contents/MacOS/myApp.
If you wish to have a command-line tool that does not use the GUI for example, moc, uic or ls, you can tell qmake to disable bundle creation from the CONFIG variable in the project file:
Deploying Applications on macOS
macOS applications are typically deployed as self-contained application bundles. The application bundle contains the application executable as well as dependencies such as the Qt libraries, plugins, translations and other resources you may need. Third party libraries like Qt are normally not installed system-wide; each application provides its own copy.
A common way to distribute applications is to provide a compressed disk image (.dmg file) that the user can mount in Finder. The deployment tool, macdeployqt (available from the macOS installers), can be used to create the self-contained bundles, and optionally also create a .dmg archive. Applications can also be distributed through the Mac App Store. Qt 5 aims to stay within the app store sandbox rules. macdeployqt (bin/macdeployqt) can be used as a starting point for app store deployment.
Note: For selling applications in the macOS App Store, special rules apply. In order to pass validation, the application must verify the existence of a valid receipt before executing any code. Since this is a copy protection mechanism, steps should be taken to avoid common patterns and obfuscate the code that validates the receipt as much as possible. Thus, this cannot be automated by Qt, but requires some platform-specific code written specifically for the application itself. More information can be found in Apple's documentation.
macOS Issues
The page below covers specific issues and recommendations for creating macOS applications.
Where to Go from Here
We invite you to explore the rest of Qt. We prepared overviews to help you decide which APIs to use and our examples demonstrate how to use our API.
- Qt Overviews - list of topics about application development
- Examples and Tutorials - code samples and tutorials
- Qt Reference Pages - a listing of C++ and QML APIs
Qt's vibrant and active community site, http://qt.io houses a wiki, a forum, and additional learning guides and presentations.
© 2020 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
